Creating/Editing a Pipeline Version
To create a new pipeline, navigate to the Search Pipelines screen using the Piplelines menu, and click on the Create button. To edit an existing pipeline, click on the Pipeline Name column of the target pipeline in the search results, or select the row and click the Edit button.
Field | Description |
|---|---|
Name | The name of the pipeline. |
Updated On | The user who last updated the pipeline verson (read-only). |
Updated By | The last update date/time of the pipeline version (read-only). |
Definition
The Definition tab provides the definition of the pipeline stages, and their steps and gates. Changes to the pipeline, like a workflow, are versioned so that changes can be published to consumers, or previous versions can be reverted.
Field | Description |
|---|---|
Description | A free-form description of the pipeline version. |
To add stages to the pipeline version, see Creating/Editing a Pipeline Stage.
Once the stages are added to the pipeline version you can reorder by clicking the arrows on the stage, or delete the stage by clicking the delete button. To view/edit the stage, click on the maximize button.
Click the button to save your changes and continue with further updates, or the button to save your changes and return to the previous page. The button reverts the changes and returns to the previous page.
Click the button to set the selected pipeline version as active, and be sure to save your changes. Upon activation, the previously active version becomes inactive. Once a version has been activated it is locked from future edits, and you must click the button to create a new version in order to make further changes. You can switch the editor to another version of the pipeline by selecting the pipeline version name in the Switch Version drop-down.
Any pipeline version which is active, or has ever been active, is locked from future edits. You must make a copy in order to make further changes.
Team
A Team defines a set of roles which will participate during execution of the pipeline. Roles assigned to the pipeline may then be used within the defined gates and steps (i.e. an approval step). A role contains default members, which can be FlexDeploy Groups, FlexDeploy Users, or email addresses (used for notifications only). A release which consumes the pipeline inherits the roles and default members from the pipeline, and can override those members. For example, the Release Manager members can be different across releases.
Tips
- Groups may not be assigned directly to gates or steps. Instead, you must create a pipeline role and assign the appropriate group as a member.
- As a best practice, avoid assigning users directly to pipeline roles. Instead, create a group with assigned users, and assign the group to the role. This allows managing users in a centralized location, and avoids management across potentially many pipelines and releases.
- Establish defaults in the role definitions of the pipeline, especially if team members are common across releases, to eliminate the need to configure the team on each and every release.
In addition to members, a role defined within a pipeline also establishes default permissions. When a release consumes the pipeline, it inherits the role's default permissions, but can override them for that particular role. In other words, a role may have different permissions from release to release if necessary.
To create a new Role, click the icon. To edit an existing Role, click on the role name. To delete a new Role, click the icon. If a role is used in older versions of the pipeline, but not the active version it will be inactivated instead of deleted.
Add FlexDeploy Group or FlexDeploy User members to the role by shuttling them from the Available lists on the left to the Member lists on the right.
Tip
Filter the list of available Groups or Users by typing all or part of its name into the Search fields.
Field | Description |
|---|---|
Name | The name of the pipeline role. |
| Manage Stage Execution | Whether or not this role has permission perform actions on the pipeline stage in the release dashboard (e.g. Replay Stage). |
| Manage Step Execution | Whether or not this role has permission perform actions on the pipeline stage step in the release dashboard (e.g. Replay Step, Skip Step). |
| Upload Execution Info | Whether or not this role has permission to upload execution information in the release dashboard (e.g. Inputs, Change Tickets). |
| Active | Indicates whether this pipeline role is active. |
| Available Groups | All FlexDeploy Groups defined within the Security. |
| Member Groups | FlexDeploy Groups assigned as members of this role. |
Available Users | All FlexDeploy Users defined within the Security. |
| Member Users | FlexDeploy Users assigned as members of this role. |
| Email Recipients | Semi-colon or comma delimited list of email addresses assigned to this role. Used for email notification only. |
Click the button to save the changes to the role (be sure to also save the pipeline, or changes will be lost), or to revert any unsaved changes.
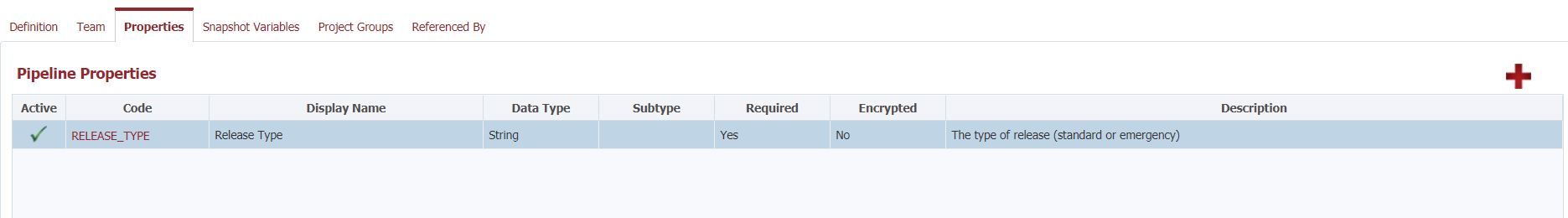
Properties
Pipeline Properties are used to decorate a release with some context. Values for the properties are provided on each release, and may be used in various groovy scripts within the pipeline definition. For example, only execute a particular step in the pipeline if the "Release Type" is "Security".
To create a new Pipeline Property, click the icon. To edit an existing Pipeline Property, click on the Property Code .
Field | Description |
|---|---|
Active | Indicates whether the pipeline property is active. Inactive properties will not appear on the release. |
| Code | A code for the property, as appropriate for variables within Groovy or Shell scripts. (e.g. no spaces or special characters other than underscore.) |
Description | A meaningful description for the property. |
| Data Type | The data type for this property. Valid types are Boolean, Double, Integer, String. |
| Subtype | Not currently used. |
| Default Value | A default value to assign to the property if not specified on the release. |
| Rows | Defines the height of the component to display when capturing the value from the user. |
| Columns | Defines the length of the component to display when capturing the value from the user. |
| Display Name | A meaningful name for the property used for display. |
| List Data | A list of valid values for the property. Optional, and only applicable for String data type. Allowed formats:
|
| Encrypted | Whether or not to encrypt the value, not display on screen or in the logs. Only applicable for String data type. |
| Multiselect | Whether multiple values can be selected from the List Data. Only applicable for String data type, and when List Data is provided. |
| Length | The maximum allowed length of the property value. Optional, and only applicable for String data type. |
| Required | Whether or not a value is required for this property. |
| Min Value | Minimum allowed value. Optional, and only applicable for Integer and Double data types. |
| Max Value | Maximum allowed value. Optional, and only applicable for Integer and Double data types. |
| Validator1 | Optional Groovy Script to validate provided value. The script should return true if the value is valid, and false otherwise. The user specified value is available to the script in the Value variable. If not valid, the ValidationMessage is displayed to the user. For example, Example if ("BAD".equals(Value)) {ValidationMessage="Bad value!!"; return false;} else {return true;}
|
| Validator2 | Optional Groovy Script to validate provided value. See Validator1. |
| Validator3 | Optional Groovy Script to validate provided value. See Validator1. |
| Validator4 | Optional Groovy Script to validate provided value. See Validator1. |
| Validator5 | Optional Groovy Script to validate provided value. See Validator1. |
Click the button to save the changes to the property (be sure to also save the pipeline, or changes will be lost), or to revert any unsaved changes.
Snapshot Variables
Snapshot variables provide state for the life of a snapshot. Such state affords the ability to store some data as part of a step or gate in one stage, and consume it or make decisions in a later stage. One classic example is to store off a CMS ticket which was entered or created in one stage, and feed it into another stage which will use the same ticket. The pipeline defines the metadata for any snapshot variables which are available, and values can be set or retrieved using Custom Gates or Custom Steps.
To create a Snapshot Variable, click on the icon. Enter the required information and click Save.
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
| Code | The identifier which is used to access the variable from Groovy |
| Active | Whether the variable is active or not. Defaults to true. |
| Description | A description for the variable. |
| Data Type | The data type of the variable. Allowed types are Boolean, Integer, Double, or String. |
Project Groups
Project Groups provide categorization tags for release content. As such, pipelines define the tags, and deploy segments of the content based on those tags. Releases consuming the pipeline can then tag its content as belonging to those groups.
For example, suppose a pipeline defines project groups Database, Configuration, and Applications. The steps within a pipeline stage can then deploy all Database, deploy all Configuration, and finally, deploy all Applications. The release which consumes the pipeline, then defines which content is tagged with Database, Configuration, and Applications.
Field | Description |
|---|---|
Active | Indicates whether the project group is active. Inactive project groups will not appear on the release or be available to the pipeline steps. |
| Code | A name for the project group. |
To add a new project group, click the icon. Enter the Group Name.
To edit a project group, modify the Group Name, or set the Active flag.
To delete a project group, click on the icon for the project group you wish to remove.
Referenced By
Identifies the Releases which are referencing this pipeline.
Field | Description |
|---|---|
Release | The internal id of the release. |
| Name | The name of the release. |
| Description | The description of the release. |
| Start Date | The start date of the release. |
| End Date | The end date of the release. |
| Status | The status of the release. |
Related content
- style