It is recommended that you use both plugins (FlexDeploy and Jenkins) together to make your projects as efficient as possible. This way you can continue to build projects using Jenkins, and also use all of the features provided by FlexDeploy. Here we'll walk through a basic example of how to use these plugins to build a project with Jenkins, and then kick off a FlexDeploy workflow that will get the finished artifact and deploy it.
Jenkins Configuration
Uploading The Plugin
First we will need to download the Jenkins FlexDeploy Plugin from here.[MAKE SURE TO MAKE THIS A LINK TO A PLACE THEY CAN GET THE PLUGIN.]
- If you downloaded the source code, you'll need to build the
.hpifile by navigating to the directory containing thepom.xmland runningmvn package.If you just downloaded the compiled
JenkinsFlexDeployPlugin.hpi, you can skip this step and just move on to step 3.
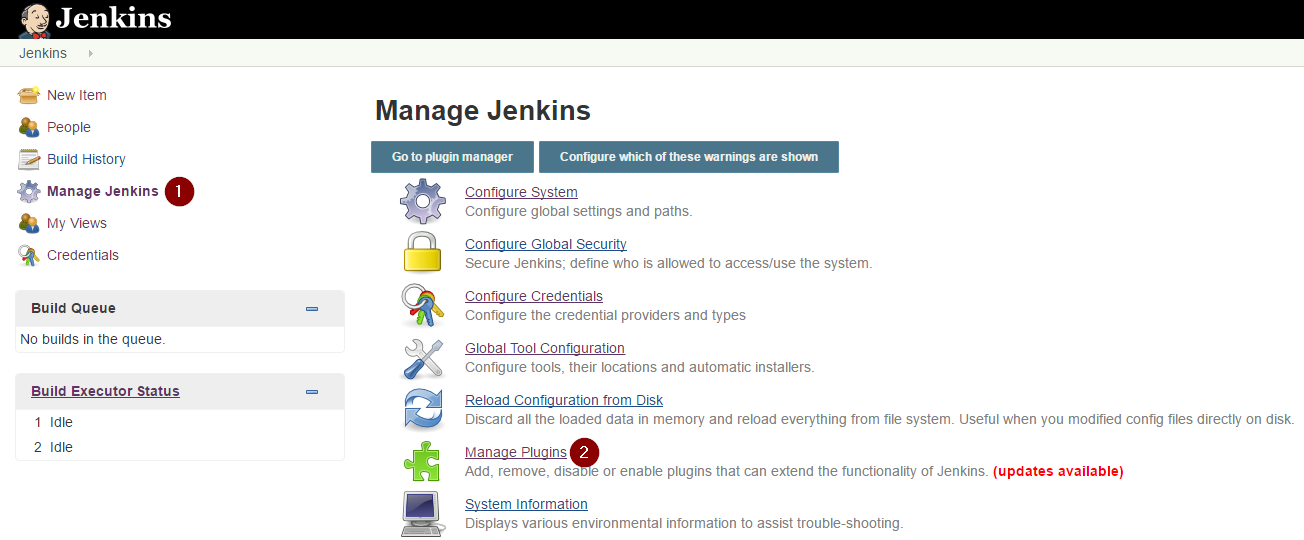
- To upload the plugin, connect to your Jenkins server and click "Manage Jenkins" then choose "Manage Plugins".
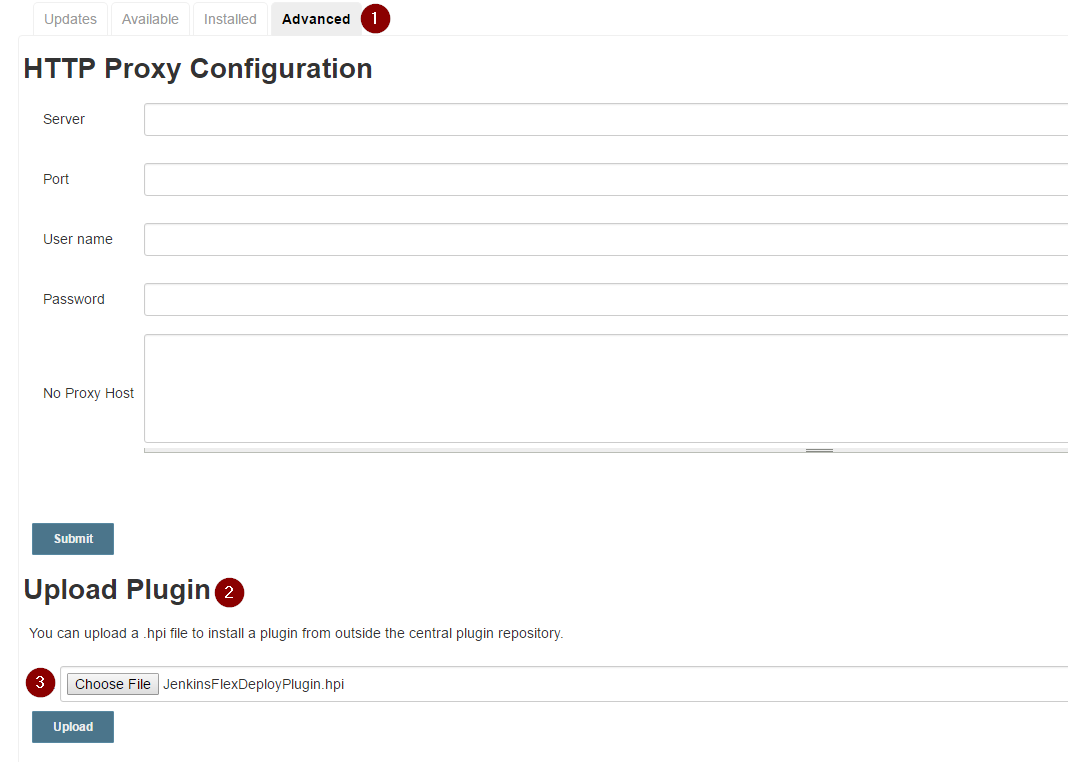
On the "Manage Plugins" page, choose the "Advanced" tab, then click "Choose File" under the "Upload Plugin" section.
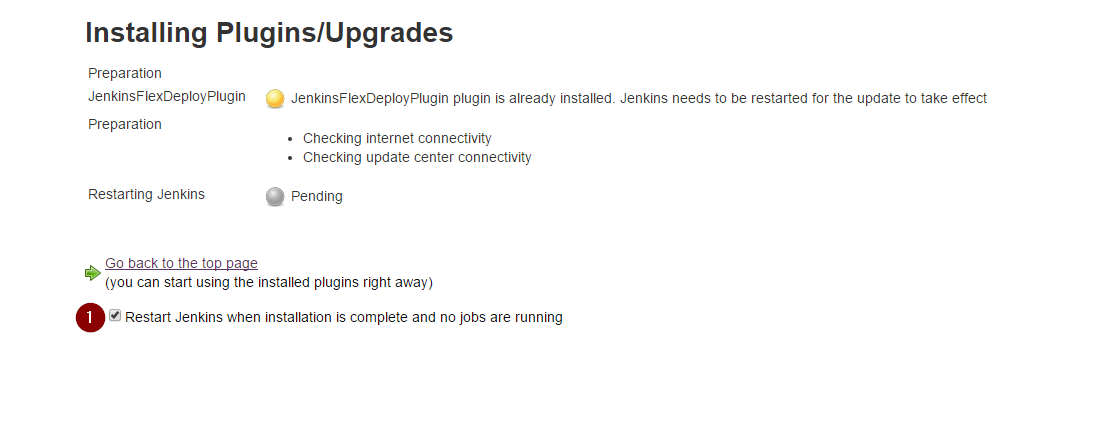
- After clicking Upload, you may need to restart the Jenkins server for the changes to take effect. Just check the box on the next screen.
Configuring the Plugin to work with FlexDeploy
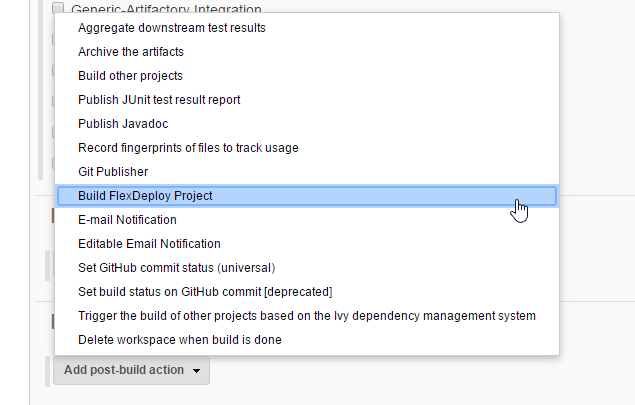
- In your Jenkins project configuration, scroll down to the "Post-Build Actions" section, and click "Add Post-Build Action".
- Choose "Build FlexDeploy Project" from the menu.
- Once you've added the Build FlexDeploy Project step, you should see a configuration page like this.
- FlexDeploy URL - This is the URL to FlexDeploy on your server.
- Qualified Project Path - I left this blank, because it will most likely be set at the individual project level.
- Environment Code - This is the environment we will be building in. I chose to use my development environment in this example, but this could be any environment code you want.
- Credentials - The credentials Jenkins should use to connect to FlexDeploy with. Can be stored using the Credentials plugin, or you can enter a username and password.
- Stream Name - This is the stream to build your FlexDeploy project in. Note that this will almost always be the default stream name, as the build workflow will probably not actually need to use it. The default value is trunk, but it should be changed to match the stream name setting in your Project Defaults configuration in FlexDeploy.
- Wait for FlexDeploy - Check this box to make the plugin remain in a 'Running' state until the FlexDeploy workflow completes, then mark the Jenkins build as failure or success based on the FlexDeploy workflow status. If workflow execution takes longer than 15 minutes, the plugin will stop polling and report success.
Test Connection Button - This button can verify that your FlexDeploy URL and Credentials are valid.
- Inputs - This section is where you would define any workflow inputs you have configured.
- Input Code - The code of the workflow input to pass in.
Value - The value to be passed in with the workflow input. You can use environment variables (Like BUILD_ID) to pass in values.
For a full list of available variables, take a look at this page.- FlexFields - This section is where you would define any build FlexFields that need to be passed in for your build.