So far in topology we have completed the following tasks:
- Created Endpoint connections to the application-tier nodes of our EBS servers
- Create four logical Environments - Development, Test, QA, and Production
- Create a logical Instance, Global EBS, and associated to our four environments
At the completion of this section, you will:
- understand the relationship between environments, instances, and endpoints
- learn how to map environment/instance combinations to physical endpoints
- learn how to configure property values for environment/instance properties
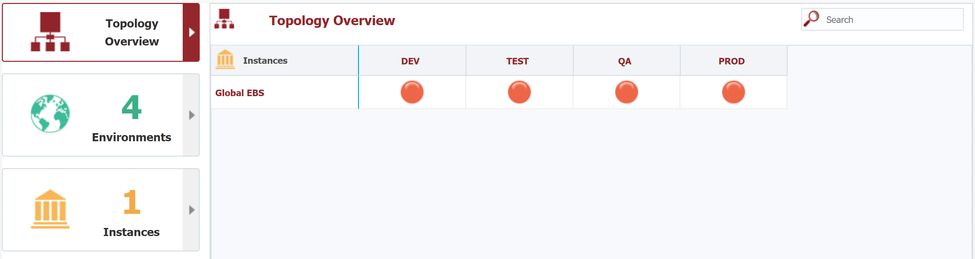
The next step is to bind the instance to the physical endpoint(s) for each environment. By associating instances to environments, a matrix is formed in the Topology Overview. To view the matrix, select Topology from the main menu, and then click on the Topology Overview from the left-hand pane.
For each environment which we mapped to our instance, a "balloon" icon appears in the matrix. Click on the balloon to map its endpoints and configure its properties.
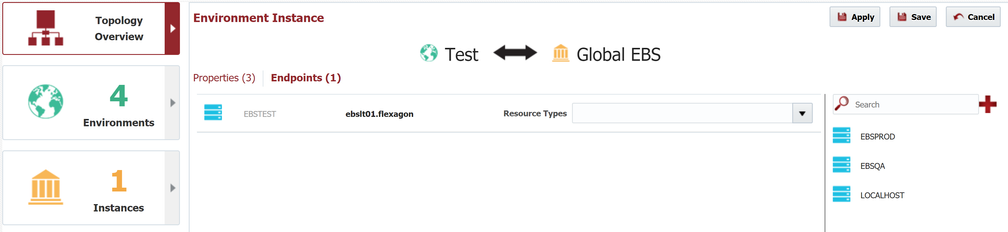
First we will configure Global EBS in Development. Click on the balloon, then select the Endpoints tab.
Since we will be sourcing our EBS customizations from GItHub we can perform the build on any endpoint. Here we will choose the LOCALHOST endpoint, which comes pre-configured with FlexDeploy installations and represents the local FlexDeploy server. SImply drag the LOCALHOST endpoint from the list of endpoints on the right-hand pane into the center pain.
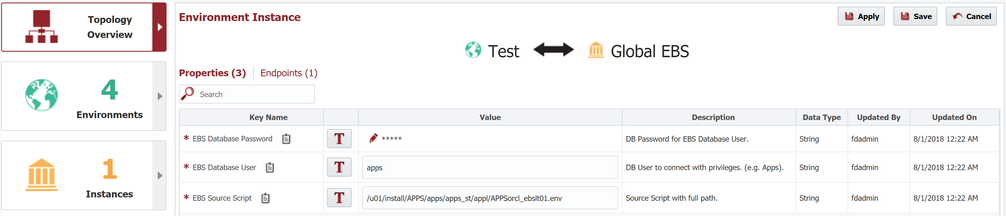
Next click on the Properties tab. Here we see the properties which are mapped to the instance. These properties are associated from workflows associated to our instance, and any plugin operations used by those workflows. We do not have any properties defined on our build and deploy workflows, but the mapped EBS plugin operations define three properties.
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| EBS Database User | The user id used to connect to the EBS database. Defaults to "apps", and would rarely be changed. |
| EBS Database Password | The encrypted password for the EBS Database User. |
| EBS Source Script | The unix source script which sets up the environment and sets a host of EBS related properties. |
Note for Development <--> Global EBS
We have mapped the LOCALHOST endpoint, which is not an EBS server. So for Development, we can simple ignore these properties.
Tip
If we were extracting the configurations from an EBS Development server we would need to perform the following activities.
- Create an endpoint for the development app-tier EBS server
- Associate this endpoint to Development ↔ Global EBS
- Set the values for the associated properties
Click Save to apply the changes.
Repeat the steps above for Test, QA, and Production. Here we will need to set values for the EBS related properties.
| Completed 6 of 10 Sections | Continue to Instance Creation | Back to Environment Creation |
|---|