At the completion of this section, you will:
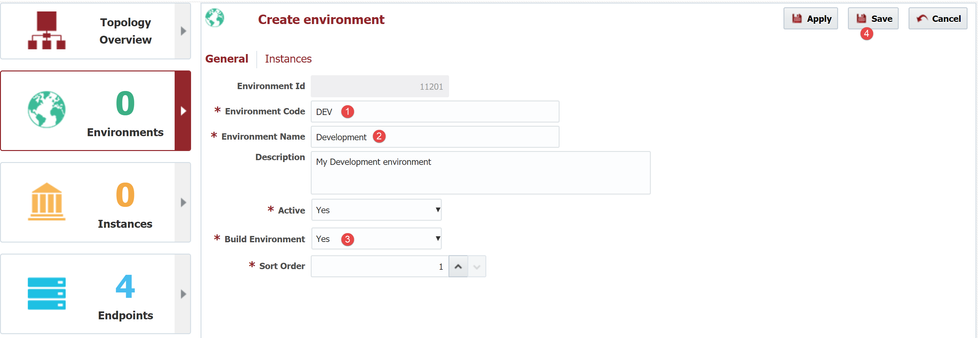
- understand the use of environments in the deployment process
- be able to create/modify an environment
An Environment is a logical name given to a group of servers, applications, and technologies which work together to provide a software solution for the purpose of development, testing, or a production implementation. Typical Environments include, but are not limited to, Development (DEV), System Integration Testing (SIT), User Acceptance Testing (UAT), and Production (PROD).
For this tutorial we will create four environments - Development, Test, QA, and Production. These environments host our physical EBS installations for our logical global EBS instance.
...
Field | Description | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Environment Code | A descriptive name for the environment. | ||
| Environment Name | A technical code, without any spaces. The codes are available as variables to shell and Groovy scripts, and therefore needs to comply with their limitations. | ||
| Build Environment | Whether or not this environment is available as a build environment.
|
First we will create the Development environment (as a Build Environment).
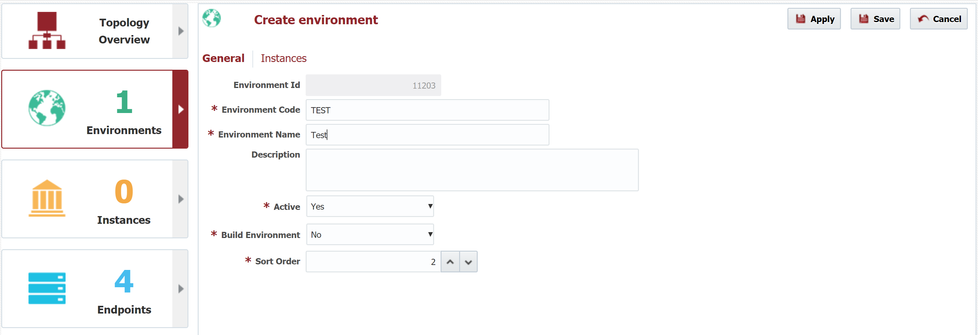
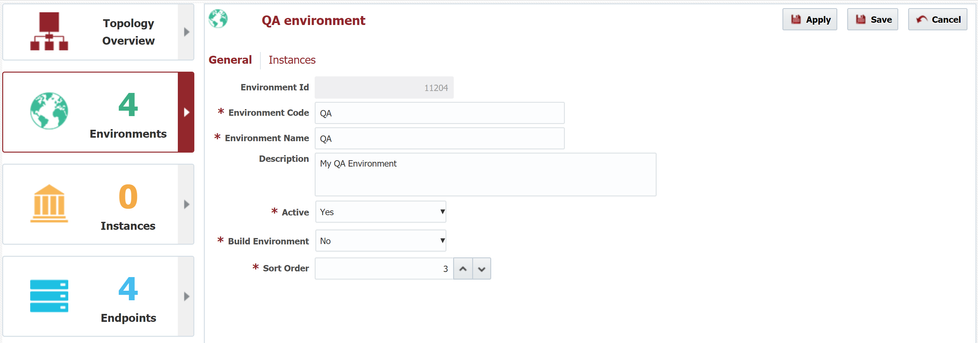
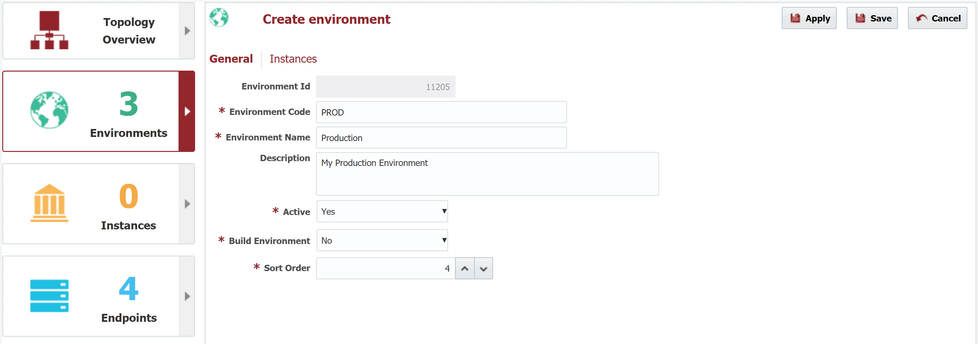
And next we will repeat the steps above for Test, QA, and Production (with Build Environment set to "No").
We now have one build environment and three deployment environments.
After creating these, the Environment screen should look like this.
| Completed 5 of 10 Sections | Continue to Environment Instance Configuration | Back to Instance Creation |
|---|
...